Faculty of Computers and Information
Minia University
Academic Year: 2025 / 2026

DuoCodo
| # | Name | Dept | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mohamed Mostafa Amer Abdelkader | CS | muhammed.mustafa.work@gmail.com |
| 2 | Mohamed Ragab Abdelhafez Mehran | CS | ragab.168926@gmail.com |
| 3 | Alaa Mohamed Abdelhakeem Ahmed | CS | alaahakeem58@gmail.com |
| 4 | Ammar Emad Ahmed Azmy Zewain | IS | za0663008@gmail.com |
| 5 | Yassin Khaled Khalaf | IS | yassenkhaled927@gmail.com |
| 6 | Marwa Farid Mohamed | IS | marwafarid366@gmail.com |
Table of Contents
List of Figures
Figure 5.38: Class Diagram - Core User and Authentication System
Figure 5.41: Class Diagram - Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
Figure 5.43: Class Diagram - Administration and Platform Management
Figure 6.1: Entity Relationship Diagram - User Management and Authentication
Figure 6.2: Entity Relationship Diagram - Learning Content and Course Structure
Figure 6.3: Entity Relationship Diagram - Submissions and Code Execution
Figure 6.4: Entity Relationship Diagram - Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
Figure 6.5: Entity Relationship Diagram - Certification and Gamification
Figure 6.6: Entity Relationship Diagram - Administration and System Management
Figure 6.7: Database Schema - User Management and Authentication
Figure 6.8: Database Schema - Learning Content and Course Structure
Figure 6.9: Database Schema - Submissions and COde Execution
Figure 6.10: Database Schema - Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
Figure 6.11: Database Schema - Certification and Gamification
Figure 6.12: Database Schema - Administration and System Management
List of Tables
- Table 2.1: Elzero Web School
- Table 2.2: Codeforces
- Table 2.3: CodeChef
- Table 2.4: HackerRank
- Table 2.5: LeetCode
- Table 2.6: TopCoder
- Table 2.7: AtCoder
- Table 2.8: CodinGame
- Table 2.9: CodeCombat
- Table 2.10: Codewars
- Table 2.11: CheckiO
- Table 3.1: Development and Operational Costs
- Table 3.2: Financial Projections
- Table 3.3: Technical Risks
- Table 3.4: Project Management Risks
- Table 3.5: Legal and Compliance Risks
- Table 5.1: Actors and Goals List
Chapter 1: Project Overview
1.1 Main Idea
We aim to create a Duolingo-inspired programming education platform that transforms how beginners learn to code by eliminating overwhelm through structured, gamified micro-lessons. Unlike fragmented resources, this platform provides a clear, progressive learning path—from core programming fundamentals to advanced topics like OOP, algorithms, and web development—all delivered via multi-format explanations (articles, videos, and guided walkthroughs).
At its core, the platform seamlessly integrates:
- An in-browser code editor (supporting Python and JavaScript) with real-time execution, syntax highlighting, and instant error diagnostics.
- Hands-on exercises featuring model solutions and optional complexity analysis to deepen understanding of code efficiency.
- XP systems, unlockable levels, daily streaks, and skill badges to reward consistency.
- Global leaderboards competitions to fuel engagement.
- Visual roadmaps highlighting completed, active, and upcoming modules.
- Mastery dashboards quantifying skill growth and retention.
By combining structured curriculum, instant feedback, and social accountability, the platform turns programming education into an addictive, confidence-building journey—making learning feel like play while ensuring tangible skill development.
1.2 Project Scope
1. Comprehensive Curriculum & Content
- Structured Learning Path:
- Tiered modules from absolute fundamentals (variables, loops) to advanced domains (OOP, algorithms, web frameworks, databases).
- Specialized tracks for Python, JavaScript, and full-stack development.
- Multi-Format Delivery:
- Concept primers: Short videos + annotated articles.
- Interactive Chat Learning: AI mascot chatbot for conversational explanations.
2. Intelligent Code Editor
- Multi-Language Support:
- Browser-based execution for Python, JavaScript, HTML/CSS, and more.
- Enhanced Developer Experience:
- Real-time syntax + error highlighting, auto-completion, and debugging hints.
- Accessibility:
- Dark/light mode, keyboard shortcuts.
3. Dynamic Interactive Exercises
- Adaptive Challenges:
- Exercises auto-adjust difficulty based on user performance.
- "Fix-the-Bug" tasks: Debug pre-written flawed code.
- Deep-Dive Analysis:
- Runtime complexity breakdowns (Big O notation).
- Memory/performance metrics for optimization practice.
- Solution Libraries:
- Model answers + multiple approach comparisons (e.g., iterative vs. recursive).
4. Advanced Gamification System
- Engagement Mechanics:
- Daily streaks, skill-specific badges (e.g., "Algorithm Ace"), and XP bonuses for consistency.
- Unlockable content: Secret lessons or tools for high achievers.
- Competitive Elements:
- Global/weekly leaderboards (XP-based).
5. Personalized Progress Ecosystem
- Learning Analytics:
- Mastery dashboards showing skill proficiency (e.g., "Data Structures: 85%").
- Time-tracking: Session duration, concepts revisited.
6. Accessibility & Scalability
- Mobile-responsive design: Seamless tablet/phone access.
- Offline mode: Download lessons/exercises for practice without internet.
1.3 Problem Statement
Learning programming remains a daunting barrier for beginners, exacerbated by four core gaps in existing solutions:
Structural Deficiency:
- Resources are fragmented (video tutorials, disjointed exercises) with no coherent progression, leaving learners adrift.
- Advanced topics (OOP, algorithms) feel inaccessible without scaffolded skill-building.
Practice-Explanation Misalignment:
- Passive video/article consumption fails to translate to coding competence.
- Feedback is delayed or absent, leading to reinforcement of errors and frustration.
Motivation Erosion:
- Isolated learning lacks psychological hooks (rewards, social accountability) to sustain consistency.
- 80% of beginners quit within 3 months due to diminishing confidence.
1.4 Solution Approach
To bridge these gaps, the platform leverages Duolingo’s engagement model fused with developer-centric depth:
A. Structured Yet Adaptive Onboarding
- Skill Tree Curriculum:
- Tiered modules map concepts from syntax basics → real-world stacks (e.g., Flask/React).
- Diagnostic quizzes auto-route learners to optimal starting points.
- Bite-Sized, Multi-Modal Lessons:
- Concepts taught via < 5-min videos, annotated snippets, and interactive sandboxes—all in one flow.
B. Contextual Practice Engine
- AI-Assisted Feedback:
- Real-time error explanations + debugging hints (e.g., “Your loop exits early: check conditionals!”).
- Exercise Evolution:
- Adaptive difficulty: Problems scale complexity based on user mastery.
- Project Sprints: Build portfolio-ready micro-apps (e.g., API-driven weather dashboard).
C. Gamification × Depth
- Progressive Unlock System:
- Earn XP/badges for accuracy, efficiency (e.g., “O(1) Solver”), and streaks.
- Competitive Depth:
- Leaderboards rank speed (solved in 30s) vs. elegance (least code lines).
- Complexity Playgrounds:
- Visualize Big O trade-offs via interactive graph comparisons (e.g., O(n²) vs. O(n log n)).
D. Personalized Reinforcement
- Predictive Roadmaps:
- Weakness-targeted challenges (e.g., “Struggling with callbacks? Try these 3 exercises!”).
- Mastery Analytics:
- Heatmaps track concept retention + time-to-proficiency across skills.
1.5 Project Objectives
1. Deliver a Progressive, Mastery-Based Curriculum
- Modular Skill Tiers: Implement 10+ competency levels (Novice → Architect) with checkpoint assessments for each tier.
- Cross-Language Tracks: Offer specialized paths for Python (Data Science/Backend), JavaScript (Frontend/Full-Stack), and Algorithms.
- Real-World Alignment: Integrate industry frameworks (e.g., React, Flask) and tools (Git, APIs) into advanced modules.
2. Build an Intelligent, Adaptive Practice Ecosystem
- AI-Driven Exercise Engine:
- Generate personalized problem sets targeting weak areas (e.g., "80% accuracy on recursion? Try these 5 challenges!").
- Auto-graded projects with rubrics for code quality, efficiency, and creativity.
- Multi-Layer Feedback:
- Provide instant syntax corrections, runtime error diagnostics, and performance benchmarks (CPU/memory usage).
3. Gamify Learning with Depth & Nuance
- Tiered Reward System:
- Award skill-specific badges (e.g., "Memory Optimizer") + rarity tiers (Bronze → Platinum).
- "Double-or-Quit" streaks: Bonus XP for consecutive days, reset on skip.
- Competitive Arenas:
- Host weekly efficiency leagues (lowest Big O wins) and speed sprints (fastest debugger).
4. Enable Hyper-Personalized Tracking
- Predictive Analytics Dashboard:
- Visualize skill decay (e.g., "Arrays mastery ↓15% in 2 weeks") and recommend refreshers.
- Track efficiency gains (e.g., "Reduced solution time by 40% this month").
- Custom Roadmapping:
- Let users build goal-oriented playlists ("Prep for FAANG Interviews" → auto-adds relevant exercises).
5. Ensure Accessibility & Scalability
Inclusive Design:
- Support screen readers, keyboard navigation, and color-blind modes.
- Offer text-to-speech explanations for complex concepts.
Infrastructure Goals:
- Offline-first capability: Download modules + editor for remote learning.
- API extensibility: Integrate with GitHub/LMS platforms for portfolio syncing.
By achieving these objectives, the platform will not only demystify programming for beginners but also cultivate a motivated, skilled community ready to tackle real-world coding challenges.
Chapter 2: Project Background
2.1 Project Background
Figma is a versatile, cloud‑based design platform widely used for crafting user interfaces, wireframes, and interactive prototypes. It enables designers and stakeholders to collaborate in real time, streamlining the design process from ideation to final output. Figma’s rich feature set — including vector editing, component‑based design, version history, and a robust plugin ecosystem — makes it central to modern UI/UX workflows. As a browser‑based tool, it removes installation barriers and ensures cross‑device accessibility.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to Figma.
Nuxt.js is a high-level framework built on Vue.js, optimized for developing server-rendered applications and static websites. It offers features like automatic routing, server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation, and a modular architecture. With built-in support for SEO, performance optimizations, and a rich community-driven ecosystem, Nuxt simplifies the development of scalable, high‑performance web apps.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to Nuxt.js.
.NET is a powerful, open-source development platform created by Microsoft for building modern, scalable, and high-performance applications. It supports multiple languages such as C#, F#, and VB.NET, and enables developers to create applications across web, desktop, mobile, cloud, and IoT environments. Known for its strong type system, robust security features, and extensive class libraries, .NET streamlines development while ensuring reliability and maintainability. With the introduction of .NET Core and now .NET 8, it offers cross-platform support and exceptional performance.
For more detailed information, you can refer to .NET.
Microsoft SQL Server is a robust, enterprise-grade relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It is designed to store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently while ensuring high performance, security, and reliability. SQL Server supports both structured query language (SQL) for relational data and JSON for semi-structured data, making it suitable for diverse modern applications. It offers advanced features such as ACID compliance, indexing, views, triggers, stored procedures, and built-in analytics through SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS). With strong support for scalability, data integrity, and transaction management, SQL Server is widely used in enterprise environments for web applications, business intelligence, and large-scale data solutions.
For more detailed information, you can refer to Microsoft SQL Server.
OpenRouter is an open‑source API platform that offers a unified interface to multiple large language models (LLMs). It enables developers to seamlessly integrate AI features—such as natural language processing, chat interfaces, and content generation—while managing authentication, fallback strategies, and cost efficiency. OpenRouter simplifies switching between or combining models from different providers.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to OpenRouter.
Gemini API is a developer-friendly interface provided by Google to access the capabilities of its Gemini family of large language models (LLMs). It allows developers to integrate advanced AI features into their applications, including natural language understanding, code generation, content summarization, and multi-modal reasoning (text, image, and more). The Gemini API is accessible through Google AI Studio and is designed to support rapid prototyping and scalable deployment of generative AI solutions. With robust security, comprehensive documentation, and seamless integration with Google Cloud, the Gemini API enables powerful, flexible AI experiences across a wide range of use cases.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to Gemini API documentation.
Monaco Editor is the highly customizable, in‑browser code editor that powers Visual Studio Code. It supports syntax highlighting, IntelliSense, code folding, and more. Lightweight yet powerful, Monaco is perfect for embedding code editing experiences within web applications such as educational platforms, developer tools, or live coding playgrounds.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to Monaco Editor.
Cloudflare is a leading web performance and security platform that provides a wide range of services to protect and accelerate websites, APIs, and applications. It acts as a reverse proxy between users and web servers, offering features such as DDoS protection, content delivery network (CDN), SSL/TLS encryption, firewall rules, and performance optimization. By caching content at global edge locations and filtering malicious traffic, Cloudflare helps improve loading speeds, reduce server load, and enhance overall security. It also offers developer tools like Cloudflare Pages and Workers for deploying scalable, serverless applications.
For more detailed imformation. you can refer to: CloudFlare.
Elzero Web School
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elzero Web School is an excellent free resource for Arabic-speaking beginners and intermediate learners who want to build strong web development skills through structured, practical learning. | - External resources and useful tool recommendations included - A Q&A section to ask questions and receive community support | - Step-by-step structured study plans for better learning flow - Dedicated learning paths for Frontend, Backend, and Full Stack | - No built-in progress tracking to monitor course completion - Users cannot rate or review courses or lessons |
Reference: https://elzero.org
Codeforces
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| A well-known platform that hosts regular contests like Div 1 and Div 2. It includes a robust rating system and editorial support to develop algorithmic thinking. | - Mathematical algorithms - Rating system - Editorial learning | - Regular contests with large community participation - Detailed editorial explanations - Transparent and active rating system | - Interface can be intimidating for beginners - Problems often require deep mathematical insight |
Reference: https://codeforces.com
CodeChef
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| An Indian educational platform hosting contests like Long Challenge and Lunchtime, with a vast problem archive and community engagement. | - Long format contests (Long Challenge) - Short contests (Lunchtime) - Tutorial-based learning | - Great for long-term learning with multiple contest formats - Offers tutorials and mentorship programs | - Sometimes suffers from server lags during contests - Problems can be less curated compared to Codeforces or LeetCode |
Reference: https://www.codechef.com
HackerRank
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focuses on algorithms, SQL, and data structures with a live coding environment, widely used for tech interviews. | - Structured learning paths - Auto-grading system - Skill-specific tracks (SQL, AI, etc.) - Live coding interface | - Beginner-friendly interface and structured learning paths - Great for practicing specific skills (e.g. SQL, AI) - Instant feedback and auto-grading | - Contest competitiveness is relatively low - Less challenging for advanced users |
Reference: https://www.hackerrank.com
LeetCode
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| A premier platform for coding interview prep with 2,500+ problems and company-specific questions. | - Interview prep questions - Company-tagged problems - Weekly contests - Solution discussions | - Focused on technical interview preparation - Community solutions and tutorials - Weekly contests to benchmark skills | - Some premium features are behind a paywall - Less emphasis on advanced algorithms |
Reference: https://leetcode.com
TopCoder
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| One of the oldest platforms, known for SRM (Single Round Matches) and Marathon Matches focusing on complex, long-term problems. | - SRM (Single Round Match) - Marathon Match - High-difficulty algorithm challenges - Real-world modeling problems | - Highly competitive and professional-grade problems - Real-world challenges and big prizes - Community of expert coders | - Interface feels outdated - Steeper learning curve for newcomers |
Reference: https://www.topcoder.com
AtCoder
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Japanese platform offering well-structured contests (ABC, ARC, AGC) with a focus on clean problem statements and difficulty progression. | - ABC, ARC, AGC contests - Clean and structured problems - Difficulty progression - On-time weekly contests | - High-quality problems and fair difficulty curve - Regular, punctual contests - Structured for serious learners | - Japanese-first interface; some translations may be rough - Smaller international community than others |
Reference: https://atcoder.jp
CodinGame
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamifies coding challenges with multiplayer and story-based games like Clash of Code and Code vs Zombies. | - Game-based problem solving - Real-time multiplayer coding - Visual programming challenges - Language flexibility (25+) | - Fun and visual way to learn coding - Supports 25+ programming languages - Great for casual or team play | - Not focused on algorithm depth - Less suitable for serious competitive programming |
Reference: https://www.codingame.com
CodeCombat
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| An RPG-style platform that teaches Python, JavaScript, and HTML through story-driven games and challenges. | - RPG-style game interface - Code-to-play mechanics - Curriculum-based learning - Beginner visual feedback | - Ideal for children and beginners - Game-based engagement with rewards - Offers structured curriculum | - Too basic for experienced developers - Some content requires a subscription |
Reference: https://codecombat.com
Codewars
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uses "Kata" - short coding exercises - to improve coding progressively with ranking and community feedback. | - Community challenge creation - Rank-based progression - Peer-reviewed solutions | - Unique ranking and progression system - Community-driven challenges and solutions - Good for practicing idiomatic code | - Lacks formal contest system - Quality of community challenges can vary |
Reference: https://www.codewars.com
CheckiO
| Description | Techniques Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offers gamified learning of Python and JavaScript through short, interactive problem-solving challenges. | - Gamified challenges - Code review mechanism - Puzzle solving - Interactive feedback | - Fun and visual interface - Encourages reviewing others' code - Python-focused challenges are especially polished | - Less suitable for advanced algorithm training - Limited language support |
Reference: https://checkio.org
2.3 Summary
In this chapter, the tools that will be used in implementation like (Node.js, Nuxt.js, Figma, Gemini API, OpenRouter, Monaco Editor, and CloudFlare). were described. Then the related work was described, (Which is listed in the previous table), and the advantages, disadvantages, and benefits of each one, then compared with the project.
Chapter 3: Feasibility and Project Planning
3.1 Feasibility Study
3.1.1 Technical Feasibility
Familiarity with Applications:
- The target learners and educators in our region are already familiar with mobile educational apps and interactive tutorials (e.g. Duolingo, Code.org) in Arabic. Using a gamified, Arabic-language interface makes the platform intuitive; users require no extra training to log in, practice coding, or track progress.
- Core team members have experience building web/mobile learning tools, so we understand typical user workflows (account setup, interactive lessons).
- Because the UI and content are in Arabic, language barriers are eliminated, further smoothing the learning curve for beginners.
Familiarity with Technology:
- Our team has strong expertise in the chosen tech stack: we have built Vue/Nuxt.js and .NET applications before and are proficient with SQL Server databases. This means we can efficiently develop the front-end UI and the back-end server.
- We have experience with embedding real-time code editors (the platform will use Microsoft’s Monaco Editor, the same engine as VS Code) and handling Python and JavaScript code execution on the server.
- We are comfortable working with AI APIs; in past projects we have integrated services (e.g. OpenAI APIs) and we can similarly use OpenRouter to connect to the Gemini API for intelligent hints. Overall, our familiarity is high and we have confidence that we have the coding, design, and integration skills needed to implement all planned features.
Project Size:
- The core team will include about 6 members (detailed below), which is appropriate for a mid-size project.
- The platform’s scope involves a moderate variety of features: a real-time code editor (supporting Python and JS), gamification mechanics (XP, badges, streaks, daily goals), AI-driven hints. This is a mid-level complexity for an experienced team.
- The development timeline is relatively tight: with a target launch by May 2026 (about 6 months from planning start), the schedule is ambitious. However, by assigning parallel sprints for front-end, back-end, and content creation, and by leveraging reusable components (Nuxt/Vue libraries, Monaco Editor, etc.), we believe the team can meet this deadline.
3.1.2 Organizational Feasibility
Project Advisor: Dr. Rehab Emad El-Dein
Champion: The development team and supervisors provide time and effort for the system.
System Users:
- Learners: Arabic-speaking students and self-learners who use the platform to learn programming through structured courses, interactive exercises, and real-time code challenges. They earn XP, badges, and streaks as they progress.
- Mentors/Instructors: More experienced developers or educators who contribute by answering questions, reviewing user code, curating content, and moderating the community. Mentors help ensure quality and provide additional support (similar to Duolingo “language mentors”).
- Administrators/Content Creators: A small team of admins who upload new course material, monitor the system, and handle technical support.
Development Team Breakdown: The team is organized into specialized roles with overlapping collaboration to ensure flexibility:
Back-end Developers (2):
Build and maintain the server-side logic in .NET, manage the SQL Server database, and implement APIs. One of the back-end developers will also take on DevOps responsibilities, handling cloud infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines, and security. Together, they will also implement real-time code execution and integration with AI APIs.Front-end Developers (2):
Develop the user interface using Nuxt.js, ensuring a responsive and intuitive design across desktop and mobile browsers. They will integrate the Monaco editor, implement gamification features (XP, badges, leaderboards), and collaborate closely with the mobile developer to keep design consistent.Mobile Developer (1):
Focuses on building and optimizing the mobile application version of the platform, ensuring a smooth experience on iOS and Android. Works with front-end and back-end teams for synchronization and performance.AI Engineer (1):
Specializes in integrating AI features, including intelligent hints and personalized feedback, through APIs like OpenRouter/Gemini. This role also explores adaptive learning models to tailor exercises to each learner’s progress.Content & Instructional Design (shared responsibility):
Instead of dedicated content creators, all team members will collaborate on producing and localizing course material in Arabic. This includes designing structured lessons, writing exercises, and embedding gamification mechanics. Team members’ technical expertise ensures content is accurate, while shared responsibility distributes workload evenly.
3.1.3 Economic Feasibility
Tangible Benefits:
- Course Revenue: With a pay-per-course model at an average price of $30 per course, enrolling 5,000 users in Year 1 (our target) would generate roughly $150,000 in Year-1 sales. As user growth continues, Year 2 and 3 revenues could be, for example, $225,000 and $300,000 (assuming 50% year-over-year user growth).
- Additional Revenue Streams: We can develop premium content or certification services in later years (e.g. advanced courses, official completion certificates) to create new revenue. Partnerships or bulk licenses with schools or companies could also add income.
- Economies of Scale: Because hosting and maintenance costs (see below) are largely fixed per year, each additional user above Year 1 yields mostly profit. For instance, once we cover the $20,000/year hosting expense and $50,000/year marketing, further enrollments significantly improve margins.
Intangible Benefits:
- Learner Engagement: The gamified, Duolingo-style approach will keep students motivated. Studies show gamification (points, streaks, badges) significantly boosts user engagement and retention. By making coding fun and rewarding, we help learners persist.
- Education Impact: Providing coding education in Arabic removes language barriers and makes computer science more accessible. This can broaden participation in tech education and help develop local talent in programming.
- Brand and Market Position: Successfully launching this platform will position our team as innovators in Arabic EdTech. Positive reputation and user testimonials will attract future investments, partnerships, and possibly expansion into new topics or markets.
Development and Operational Costs (Years 0–3):
| Item | Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development (one-time) | $280,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $280,000 |
| Dev team salaries | $180,000 | – | – | – | $180,000 |
| Content creation | $100,000 | – | – | – | $100,000 |
| Hosting/AI/maint. | $0 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $60,000 |
| Marketing | $0 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $150,000 |
| Total Cost | $280,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $490,000 |
ROI and Cumulative Net:
| Metric | Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $0 | $150,000 | $225,000 | $300,000 | $675,000 |
| Total Cost | $280,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $490,000 |
| Net Profit | -$280,000 | $80,000 | $155,000 | $230,000 | $185,000 |
| Cumulative Net | -$280,000 | -$200,000 | -$45,000 | $185,000 | — |
3-Year ROI: $185,000 ÷ $490,000 ≈ 37.8%
Break-even Analysis
The break-even point occurs when cumulative revenue surpasses cumulative costs:
- Year 1: Cumulative revenue = $150,000, cumulative cost = $350,000 → still negative (-$200,000).
- Year 2: Cumulative revenue = $375,000, cumulative cost = $420,000 → still negative (-$45,000).
- Year 3: Cumulative revenue = $675,000, cumulative cost = $490,000 → positive cumulative net ($185,000).
Therefore, the project is expected to break even during Year 3, after which all additional revenue contributes to profit.
To illustrate:
- Break-even revenue threshold: $490,000 (total 3-year cost).
- Achieved at ~16,333 paid enrollments (490,000 ÷ $30).
- Based on projected growth, this milestone will be reached in the third year of operation.
3.2 Risk Management
This section identifies key risks for the coding education platform across technical, operational, and legal domains. Each risk is assessed with a likelihood (Low/Medium/High), impact (Low/Medium/High), and mitigation strategies. Where appropriate, a qualitative risk matrix is used to emphasize prioritization.
3.2.1 Technical Risks
| Risk | Description | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scalability & Uptime | High traffic or data growth could overwhelm the platform. Without modular architecture and robust testing, performance bottlenecks and downtime can occur. | High | High | Design a scalable, microservices-based architecture; use horizontal scaling (load balancing, CDN, caching); implement automated testing and monitoring to detect and prevent bottlenecks. |
| External API Integration | Reliance on third-party APIs (e.g. Gemini, OpenRouter) can introduce outages or unpredictable behavior. Third-party services may have downtime or breaking changes. | Medium | High | Vet and monitor external APIs closely (uptime/SLA checks); implement timeouts and retries; use circuit breakers to protect against surges; prepare fallback or degraded modes if an API fails. |
| Real-time Code Execution | Running user-submitted code in real time is error-prone. Sandbox failures, resource exhaustion, or vulnerabilities could crash the executor, harming reliability. | Medium | High | Isolate execution in secure sandboxes or containers; enforce resource limits (memory/time); continuously test with diverse workloads; scale the execution engine separately; monitor and auto-recover. |
3.2.2 Operational Risks
| Risk | Description | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline Delays | Requirement changes, scope creep, or underestimation can derail schedules. Over-optimistic estimates may lead to extended deadlines. | High | High | Use thorough upfront planning and clear requirements; apply realistic time estimates with contingency; use agile sprints for incremental delivery and reviews. |
| Resource Constraints | Limited team size or skill shortages create bottlenecks. | Medium | High | Cross-train staff and onboard talent early; use contingent resources; maintain a pipeline of developers; forecast and reallocate workloads proactively. |
| Content Development Bottlenecks | Creating high-quality, engaging coding lessons and exercises is time-consuming, which can delay releases or reduce quality. | Medium | Medium | Develop content iteratively with SMEs; reuse or adapt existing materials; employ instructional designers; prioritize high-impact modules first. |
3.2.3 Legal & Compliance Risks
| Risk | Description | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy (Minors) | Collecting data on children raises strict legal requirements (e.g., COPPA, GDPR). Failure to comply can cause severe penalties. | Medium | High | Apply "privacy by design": minimize data collection, encrypt sensitive data, obtain parental consent, maintain clear privacy policies, and conduct regular audits. |
| Copyright & Licensing | Using third-party or community code/assets risks license infringement. Even one noncompliant license could result in legal or financial penalties. | Low | Medium | Enforce strict review of all content/code; use license scanners; prefer permissive or original content; educate users on plagiarism; remediate infringing material. |
| Terms-of-Service Violations | Users may post disallowed content (hate speech, copyrighted code, malicious submissions) or cheat, violating the platform's ToS. | Medium | Medium | Publish comprehensive ToS; implement moderation and reporting tools; enforce rules via filters and manual review; respond promptly and revise policies regularly. |
3.3 Project plan
TO DO
3.4 Gantt Chart
TO DO
Chapter 4: System Analysis
4.1 Function Requireements
4.1.1 User Management System
User Registration and Authentication
- FR-1.1: System shall allow users to create accounts using email, username, and password.
- FR-1.2: System shall support social login (Google, GitHub) for quick registration.
- FR-1.3: System shall implement email verification for new accounts.
- FR-1.4: System shall provide secure password reset functionality via email.
- FR-1.5: System shall enforce strong password policies (minimum 8 characters, special characters).
- FR-1.6: System shall implement two-factor authentication (2FA) as an additional security feature.
User Profiles and Settings
- FR-1.7: System shall allow users to create and edit personal profiles with avatar, bio, and learning goals.
- FR-1.8: System shall allow users to select preferred programming languages (Python, JavaScript, etc.).
- FR-1.9: System shall support multiple language interface options (Arabic, English).
User Roles and Permissions
- FR-1.10: System shall support multiple user roles: Learner, Administrator, Content Creator.
- FR-1.11: System shall implement role-based access control for different platform features.
4.1.2 Learning Management System
Course Structure and Navigation
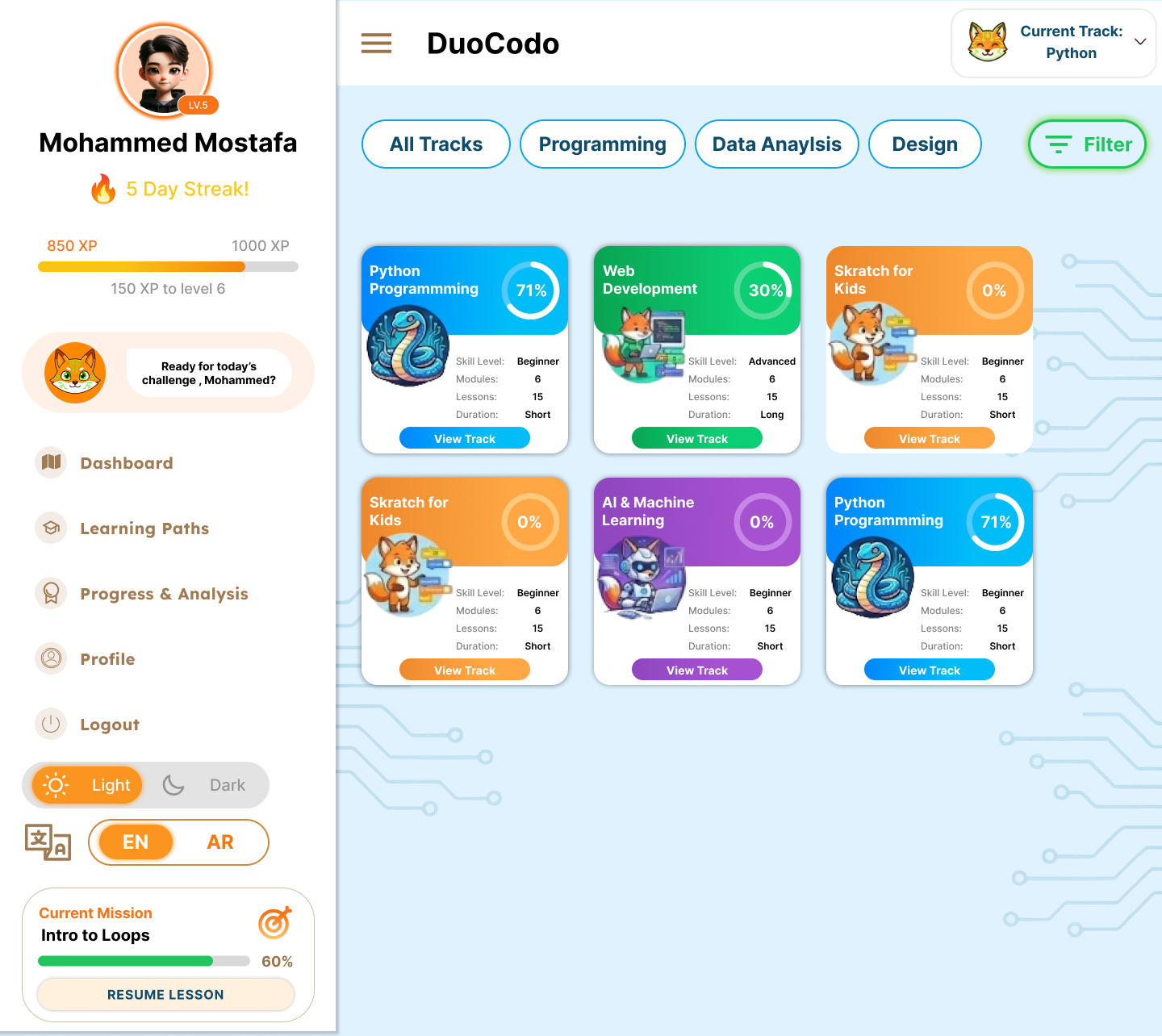
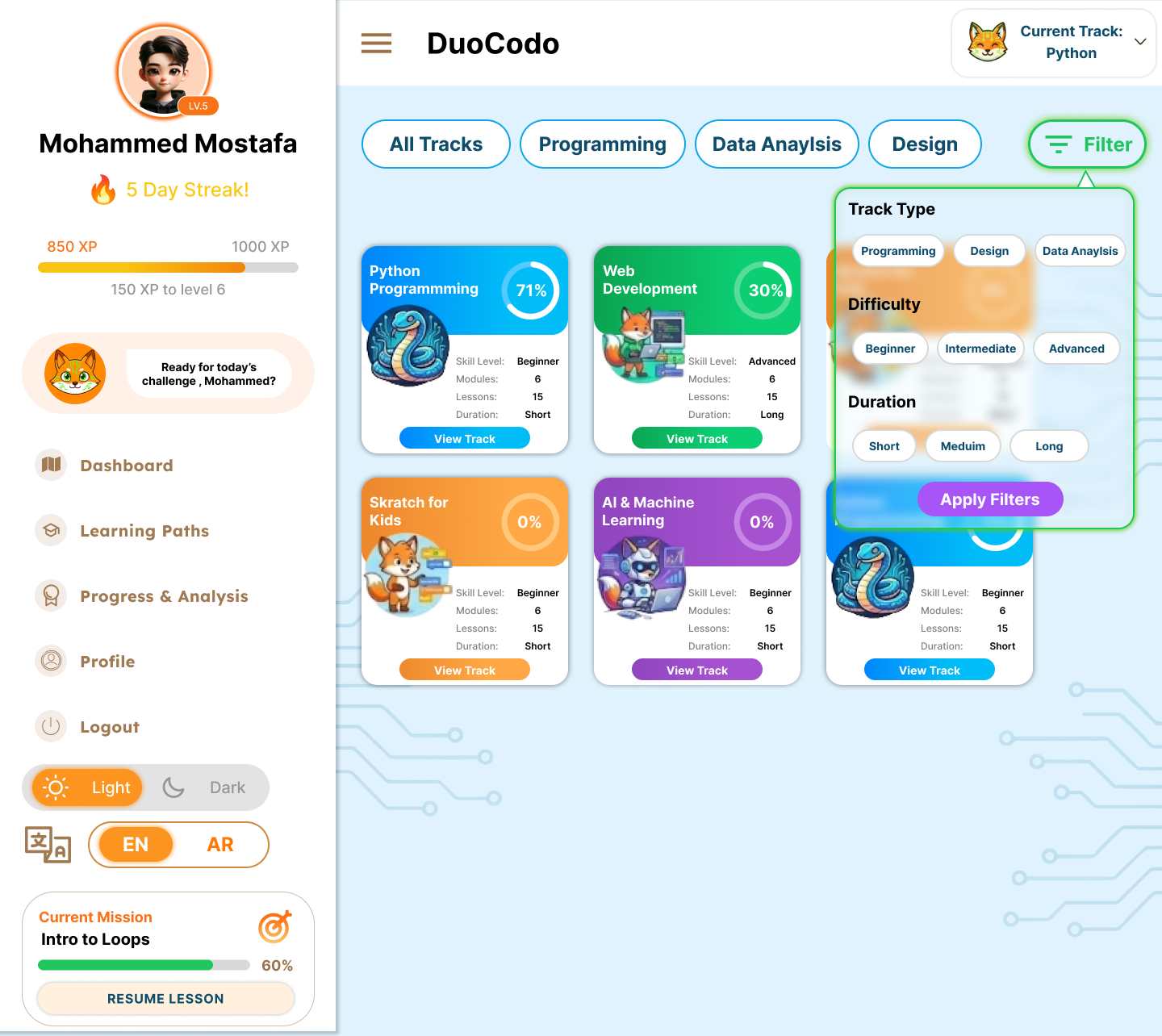
- FR-2.1: System shall organize content into structured learning paths from fundamentals to advanced topics.
- FR-2.2: System shall implement prerequisite-based lesson unlocking mechanisms.
- FR-2.3: System shall provide a visual learning roadmap showing completed, current, and locked modules.
- FR-2.4: System shall support multiple learning tracks (Python, JavaScript, Web Development, OOP, Algorithms).
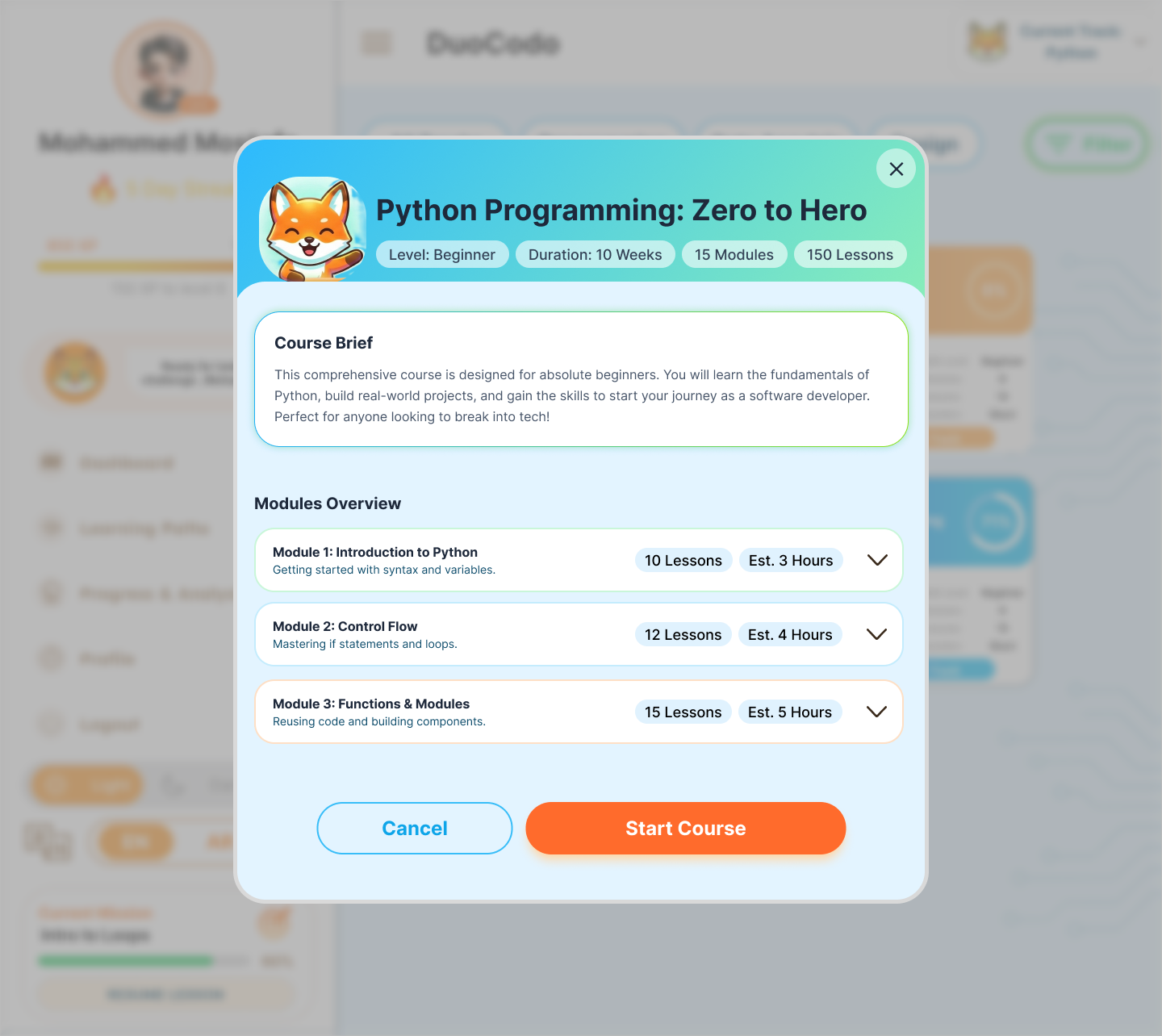
Lesson Content Delivery
- FR-2.5: System shall support multi-format lesson content (text, videos, interactive demos).
- FR-2.6: System shall provide step-by-step coding walkthroughs with highlighted code segments.
- FR-2.7: System shall include conceptual explanations before practical exercises.
- FR-2.8: System shall support rich text formatting, code syntax highlighting, and embedded media.
Adaptive Learning Features
- FR-2.9: System shall track user performance and recommend personalized learning paths.
- FR-2.10: System shall adjust exercise difficulty based on user success rates.
- FR-2.11: System shall provide spaced repetition reminders for previously learned concepts.
4.1.3 Code Editor and Execution Environment
In-Browser Code Editor
- FR-3.1: System shall embed Monaco Editor for in-browser code editing.
- FR-3.2: System shall support syntax highlighting for Python, JavaScript, etc.
- FR-3.3: System shall provide auto-completion and IntelliSense features.
- FR-3.4: System shall include line numbering, code folding, and bracket matching.
- FR-3.5: System shall support multiple editor themes (dark/light mode).
- FR-3.6: System shall provide keyboard shortcuts for common coding operations.
Code Execution and Testing
- FR-3.7: System shall execute user code securely using APIs.
- FR-3.8: System shall display real-time output and error messages.
Code Analysis and Feedback
- FR-3.9: System shall provide instant syntax error detection and suggestions.
- FR-3.10: System shall offer code optimization suggestions and best practices.
- FR-3.11: System shall compare user solutions with model answers.
- FR-3.12: System shall highlight potential bugs or logical errors using LLM.
Blockly Integration
- FR-3.13: System shall provide a block-based workspace with customizable categories (Logic, Math, Control, Events, etc.).
- FR-3.14: System shall allow users to generate source code (JavaScript/Python) from block structures.
- FR-3.15: System shall enable code execution within the application environment.
- FR-3.16: System shall support saving and loading block configurations in XML/JSON format.
4.1.4 Interactive Exercise System
Exercise Types and Structure
- FR-4.1: System shall support coding challenges, bug fixing, code completion, and multiple-choice exercises.
- FR-4.2: System shall provide clear problem statements with input/output examples.
- FR-4.3: System shall include starter code templates when appropriate.
- FR-4.4: System shall support progressive difficulty within exercise sets.
- FR-4.5: System shall offer optional hints and explanations.
Validation and Grading
- FR-4.6: System shall automatically validate solutions against test cases.
- FR-4.7: System shall track solution attempts and provide retry mechanisms.
Solution Management
- FR-4.8: System shall provide "section of solutions" after successful completion.
- FR-4.9: System shall allow users to submit multiple approaches to the same problem.
4.1.5 Gamification System
Points and Experience (XP)
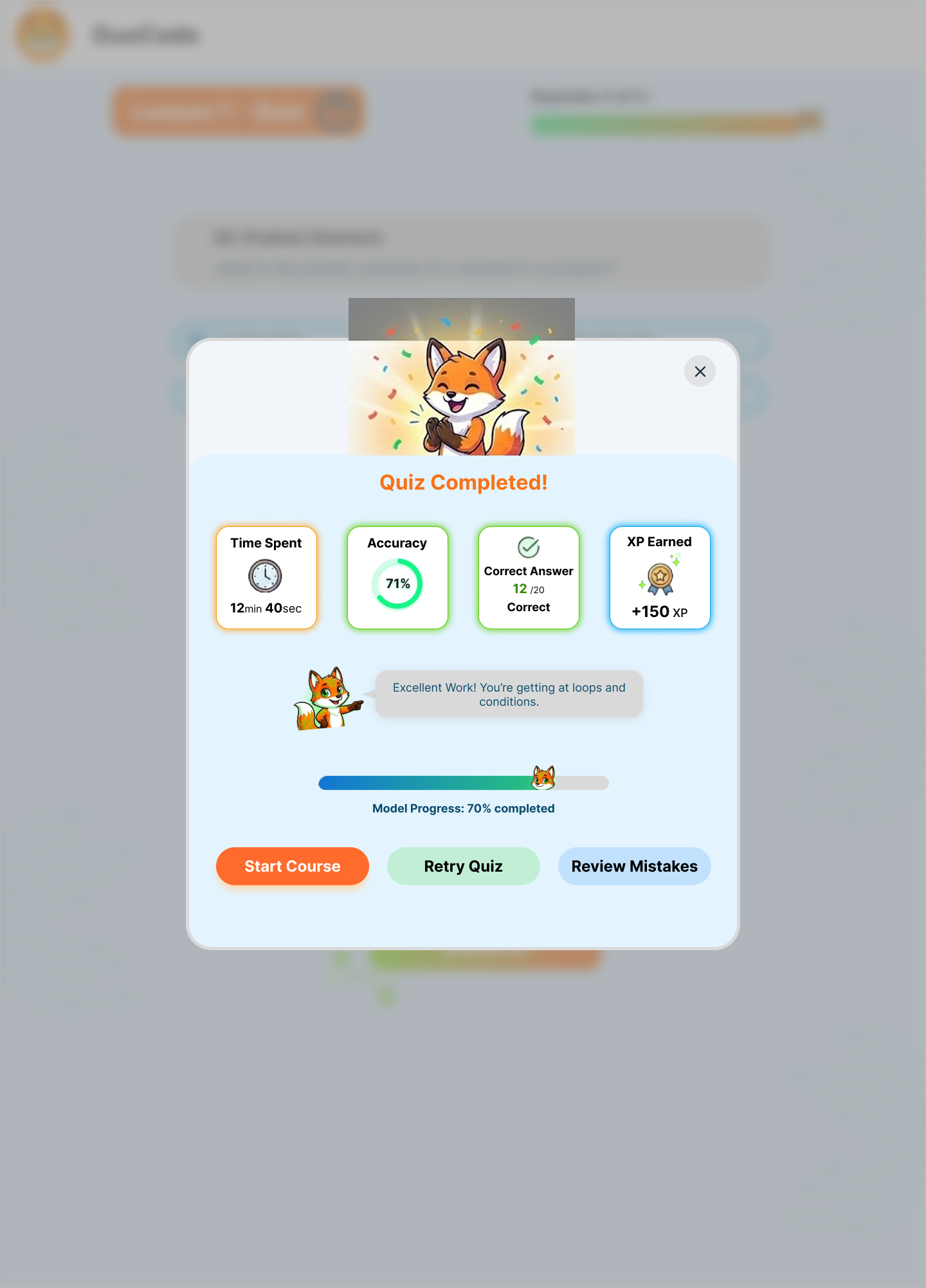
- FR-5.1: System shall award XP for completed lessons, exercises, and achievements.
- FR-5.2: System shall implement progressive XP requirements for level advancement.
- FR-5.3: System shall provide XP bonuses for consecutive learning streaks.
- FR-5.4: System shall award bonus points for first attempts.
- FR-5.5: System shall display XP progress bars and level indicators.
Achievement System
- FR-5.6: System shall implement badge categories (completion, mastery, collaboration).
- FR-5.7: System shall provide rare and legendary badges for exceptional achievements.
- FR-5.8: System shall display badge galleries on user profiles.
- FR-5.9: System shall notify users upon earning new achievements.
Leaderboards and Competition
- FR-5.10: System shall maintain global and weekly leaderboards.
- FR-5.11: System shall support friend-based leaderboards and challenges.
- FR-5.12: System shall provide leaderboard filtering by time, skill level, or language.
Streaks and Daily Goals
- FR-5.13: System shall track daily learning streaks with visual indicators.
- FR-5.14: System shall send streak reminder notifications.
- FR-5.15: System shall provide streak recovery options.
Certification Management
- FR-5.16: System shall display all available certifications with details.
- FR-5.17: System shall allow eligible users to enroll in certification tracks.
- FR-5.18: System shall create a certification dashboard showing progress and deadlines.
4.1.6 Progress Tracking and Analytics
Individual Progress Monitoring
- FR-6.1: System shall maintain comprehensive learning history per user.
- FR-6.2: System shall calculate and display skill mastery percentages.
- FR-6.3: System shall track time spent on topics and exercises.
- FR-6.4: System shall identify strengths and weaknesses.
Performance Analytics
- FR-6.5: System shall track accuracy rates and improvement trends.
- FR-6.6: System shall monitor learning velocity.
- FR-6.7: System shall calculate estimated completion time for coursework.
Visual Progress Representation
- FR-6.8: System shall provide interactive progress roadmaps.
- FR-6.9: System shall display skill trees showing mastered and locked concepts.
4.1.7 AI-Powered Features
Intelligent Hints and Assistance
- FR-7.1: System shall integrate AI APIs (Gemini via OpenRouter) for contextual hints.
- FR-7.2: System shall provide progressive hint levels.
- FR-7.3: System shall analyze user code and suggest improvements.
- FR-7.4: System shall generate explanations for complex programming concepts.
- FR-7.5: System shall adapt hint complexity based on user skill.
Personalized Learning Recommendations
- FR-7.6: System shall suggest relevant exercises when users struggle.
Automated Content Generation
- FR-7.7: System shall generate variations of exercises for extra practice.
- FR-7.8: System shall generate code examples for abstract concepts.
4.1.8 Content Management System
Course and Lesson Administration
- FR-8.1: System shall provide a content creation interface for authorized users.
Exercise and Assessment Management
- FR-8.2: System shall allow creation of coding exercises with test cases.
- FR-8.3: System shall support exercise difficulty categorization.
- FR-8.4: System shall validate exercises before publication.
Multimedia Content Support
- FR-8.5: System shall support video upload or embedding.
- FR-8.6: System shall support content localization for multiple languages.
4.1.9 System Administration
User Management
- FR-9.1: System shall provide an administrative dashboard for managing user accounts.
- FR-9.2: System shall support user role assignment and permission management.
Platform Monitoring and Analytics
- FR-9.3: System shall maintain system logs and audit trails.
- FR-9.4: System shall provide usage statistics and dashboards.
Content Moderation
- FR-9.5: System shall support manual content review and moderation workflows.
- FR-9.6: System shall maintain content removal and user warning systems.
4.1.10 Integration and API Features
Third-Party Integrations
- FR-10.1: System shall integrate with external authentication providers (OAuth or BetterAuth).
- FR-10.2: System shall connect with AI services (OpenRouter, Gemini API).
Platform APIs
- FR-10.3: System shall provide RESTful APIs for web and mobile apps.
- FR-10.4: System shall support webhook integrations.
Mobile and Cross-Platform Support
- FR-10.5: System shall deliver a responsive web interface optimized for mobile.
- FR-10.6: System shall provide mobile-specific features (push notifications).
- FR-10.7: System shall ensure cross-browser compatibility.
4.1.11 Security and Privacy
Data Protection
- FR-11.1: System shall encrypt sensitive user data at rest and in transit.
- FR-11.2: System shall implement secure session management and timeouts.
- FR-11.3: System shall provide privacy controls and data deletion options.
- FR-11.4: System shall comply with GDPR and COPPA standards.
Platform Security
- FR-11.5: System shall implement input validation and sanitization.
- FR-11.6: System shall protect against XSS, CSRF, and SQL injection.
- FR-11.7: System shall secure API endpoints with authentication and authorization.
- FR-11.8: System shall implement rate limiting and DDoS protection.
4.2 Non-Function Requirements
4.2.1 Performance
NFR-1.1: Response Time
- Landing page load: 2 seconds (3G or better)
- Monaco editor initialization: 3 seconds
- Code execution results: 5 seconds (standard exercises)
- API responses: 1 second (login, save, submit)
- Search/filtering: 2 seconds
NFR-1.2: Throughput
- Concurrent users: 1,000+ without degradation
- Simultaneous code executions: 500+
- Peak submissions: 10,000/hour
NFR-1.3: Resource Utilization
- Client memory: ≤ 500MB
- Monaco editor: ≤ 200MB
- Database queries: 100ms (95% of operations)
- CDN cache hit rate: 90%+
NFR-1.4: Rendering Performance
- Interactive elements response: 100ms
- Animation frame rate: 60 FPS
- Roadmap rendering (100 nodes): 1.5 seconds
4.2.2 Availability
NFR-2.1: System Uptime
- Annual uptime: 99.5% (~43.8 hours downtime)
- Maintenance windows: ≤ 4 hours/month (low-usage periods)
NFR-2.2: Service Availability
- Core features: 24/7 availability
- AI hints: 95% uptime
- Leaderboards: 98% uptime
NFR-2.3: Geographic Availability
- Global accessibility with focus on Arabic-speaking regions
NFR-2.4: Graceful Degradation
- AI unavailable → pre-generated hints available
- Execution service down → lessons & content accessible
4.2.3 Scalability
NFR-3.1: Horizontal Scalability
- Stateless architecture for seamless load balancing
- Connection pooling for efficient resource management
NFR-3.2: User Growth
- Year 1: 50,000 users
- Year 3: 200,000 users (without major changes)
NFR-3.3: Content Scalability
- Launch: 500 lessons, 5,000 exercises
- Future: 2,000 lessons, 20,000 exercises
- Support new languages without refactoring
NFR-3.4: Database Scalability
- PostgreSQL with read replicas
- Quarterly query plan reviews
4.2.4 Reliability
NFR-4.1: Error Rate
- System error rate: <0.5%
- Code execution failures: <1% (system errors only)
NFR-4.2: Data Integrity
- ACID compliance for progress data (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
- Daily backups with 30-day point-in-time recovery
NFR-4.3: Fault Tolerance
- No single point of failure
- Database failover: 60 seconds automatic
NFR-4.4: Data Consistency
- Leaderboards: eventual consistency within 5 minutes
- User profiles: immediate consistency
- Cache invalidation: 30 seconds
4.2.5 Interoperability
NFR-5.1: API Standards
- RESTful design with standard HTTP methods
- JSON responses with consistent structure
- OpenAPI/Swagger documentation
NFR-5.2: Third-Party Integration
- OAuth 2.0 (Google, GitHub)
- Webhook support with JSON payloads
NFR-5.3: Data Exchange
- Export formats: JSON, CSV
- Version-control compatible storage
NFR-5.4: Browser Compatibility
- Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge (latest versions)
- Browsers released within 2 years
NFR-5.5: Mobile Compatibility
- Responsive: 320px–2560px
- Native notifications (FCM/APNs)
4.2.6 Usability
NFR-6.1: Learnability
- Account setup → first lesson: 5 minutes
- Interactive tutorial: <10 minutes
NFR-6.2: UI Design
- Material Design principles
- Arabic (RTL) and English (LTR) support
- 3 font size options
NFR-6.3: Accessibility
- Keyboard navigation (tab, arrows, enter)
- ARIA labels and semantic HTML
- Color-blind modes with alternative indicators
NFR-6.4: Error Handling
- User-friendly messages (Arabic/English)
- Contextual help tooltips
- Searchable help center accessible from all pages
NFR-6.5: Localization
- Full Arabic/English localization
- Language switching without progress loss
- Regional date, time, and number formatting
NFR-6.6: Responsiveness
- Immediate visual feedback
- Progress indicators for operations > 1 second
4.2.7 Maintainability
NFR-7.1: Code Quality
- Test coverage: ≥ 80% (critical components)
- Peer review required before merge
NFR-7.2: Documentation
- API docs with examples and schemas
- Architecture diagrams (system, database, data flow)
- Code comments for complex logic
NFR-7.3: Modularity
- Reusable, independently testable components
- Versioned migration scripts
NFR-7.4: Logging & Monitoring
- Centralized logs with 90-day retention
- Automated alerts for critical errors
NFR-7.5: Deployment
- Automated CI/CD pipelines
- Rollback capability: 10 minutes
4.2.8 Recovery
NFR-8.1: Backup & Restore
- Daily full + 6-hour incremental backups
- 30-day point-in-time recovery
- Weekly integrity verification
NFR-8.2: Disaster Recovery
- Semi-annual testing
- RTO: 4 hours
- RPO: ≤ 1 hour data loss
NFR-8.3: Failure Detection
- Alert within 2 minutes of critical failure
NFR-8.4: Data Recovery
- Individual account restoration
- Checksum validation with automatic rollback
NFR-8.5: Service Recovery
- Resume after maintenance: 5 minutes
- Automatic session restoration
- Clear incident messaging
NFR-8.6: Transaction Recovery
- Automatic completion or manual review
- Transaction log maintenance
4.3 Functional Decomposition
Decomposition Diagram - Part 1
Decomposition Diagram - Part 2
Chapter 5: System Architecture
5.1 Actor-goal List
| Actor | Goals |
|---|---|
| Learner | 1. Register, log in, and manage their own profiles. 2. Choose preferred programming languages and interface languages. 3. Follow structured learning paths and unlock lessons progressively. 4. Learn via text, videos, and interactive demos. 5. Practice coding using Monaco Editor with syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and real-time feedback. 6. Receive AI-powered hints, explanations, and recommendations. 7. Complete exercises, earn XP, badges, and certifications. 8. Track progress, mastery, and performance analytics. 9. Participate in leaderboards, streaks, and challenges. |
| Content Creator / Instructor | 1. Create and manage courses, lessons, and coding exercises. 2. Categorize exercises by difficulty and validate before publishing. 3. Add multimedia (videos, images) and localized content. 4. Review and update educational materials. 5. Generate content in different formats (text, code, interactive demos). |
| Administrator | 1. Manage user accounts and assign roles/permissions. 2. Monitor platform analytics and logs. 3. Moderate content and enforce warnings or removals. 4. Oversee data security, backups, and system performance. "-" 5. Configure integrations and APIs for external services. "-" |
| AI System (Gemini / OpenRouter) | 1. Provide contextual hints and adaptive learning recommendations. 2. Analyze learner code to detect errors and suggest improvements. 3. Generate additional exercises and code examples. "-" 4. Adjust hint complexity based on user skill level. "-" |
5.2 Use Cases Diagram
5.3 Use Cases Format
This section presents use cases for the DuoCodo platform organized by user role. The cases progress from administrative functions through content creation to learner interactions, using three format levels: Brief (one-line), Casual (structured scenarios), and Fully Dressed (comprehensive specifications).
5.3.1 Administrator Use Cases
Brief Format Use Cases
Casual Format Use Cases
Fully Dressed Format Use Cases
- The visual path designer must support drag-and-drop for organizing tiers.
- The system must prevent circular dependencies through real-time validation.
- Administrator must be able to visualize the entire path structure at a glance.
- All creator assignments must be logged with timestamps.
- System must send automated reminders to creators as deadlines approach.
- Content creation progress must be trackable in real-time.
- Administrators must be able to export path structure as PDF for documentation.
- The system must support versioning for path updates.
- All prerequisite logic must be clearly documented and testable.
- System must handle paths with 50+ courses without performance degradation.
- Path analytics must aggregate data without exposing individual learner privacy.
- Paths must support localization for international audiences.
5.3.2 Content Creator Use Cases
Brief Format Use Cases
Casual Format Use Cases
Fully Dressed Format Use Cases
- All data must be auto-saved every 2 minutes to prevent loss.
- Draft exercises are only visible to the creator.
- Model solutions must be encrypted in database.
- System must support Python, JavaScript, and eventually Java/C++.
- Problem statements must pass basic grammar check before saving.
- Exercise creation interface must be accessible via keyboard navigation.
- Validation must complete within 60 seconds for standard exercises.
- All validation checks must be logged for quality assurance auditing.
- Validation must detect common anti-patterns (hardcoded solutions, trivial test cases).
- System should cache validation results; re-validation only needed if exercise changes.
- Validation API must handle concurrent requests from multiple creators.
- Failed validations must provide actionable guidance, not just error messages.
- Warnings must be clearly documented for peer reviewers.
- Reviewer recommendations must consider expertise, workload, and reliability.
- System must prevent assigning reviewers who have conflicts of interest.
- The task board must clearly show progress and remaining work.
- Creators must be able to save work-in-progress at any time (auto-save every 2 minutes).
- System must support version history for all created content.
- Communication between creator and administrator must be logged.
- Deadline reminders must be sent at 7 days, 3 days, and 1 day before due date.
- Content submission must include a checklist confirmation (all requirements met).
- Administrator feedback must be clear, actionable, and specific.
5.3.3 Learner Use Cases
Brief Format Use Cases
Casual Format Use Cases
Fully Dressed Format Use Cases
- 2FA codes must expire after 30 seconds (standard TOTP protocol).
- Backup codes must be cryptographically secure random strings.
- The system must support time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) standard.
- SMS delivery must occur within 60 seconds.
- Recovery codes must be hashed in the database, not stored in plain text.
- The system must rate-limit 2FA verification attempts (max 5 per 15 minutes).
- All 2FA setup and verification events must be logged for security auditing.
- Code Editor must load within 2 seconds
- Editor must support Python 3.10+ and ES6+ JavaScript
- Code execution must complete within 5 seconds for standard exercises
- The sandbox environment must prevent:
- File system access
- Network requests
- System command execution
- Resource exhaustion attacks
- All code submissions must be encrypted during transmission (TLS 1.3)
- The editor must be fully keyboard-accessible (WCAG 2.1 AA compliant)
- Dark and light themes must both have sufficient contrast ratios
- Editor must work on screens as small as 1024x768
- Auto-save must occur every 30 seconds
- Maximum code file size: 10,000 lines
- Support for multiple programming languages must be extensible
- Blocks shake and show red outline
- Tooltip displays: "❌ Cannot connect: Expected NUMBER, got TEXT"
- Blocks bounce back to original position
- Learner must use correct block type
- Incomplete blocks flash yellow
- "Run Code" button is disabled until complete
- Hint suggests which category has needed blocks
- Execution is terminated after 3 seconds
- System displays:
- Problematic loop block is highlighted in red
- Learner can review loop logic
- System displays error in simple terms:
- Problematic block glows red
- Learner can tap block for more details
- System shows which tests failed:
- Learner can revise blocks and retry
- "Undo" button appears for 5 seconds
- Tapping "Undo" restores deleted blocks
- After 5 seconds, deletion is permanent
- Learner can recreate blocks from toolbox
- System saves current block positions
- Re-layouts workspace for new orientation
- Portrait mode: Toolbox becomes bottom drawer
- Landscape mode: Toolbox on left sidebar
- All blocks remain in same relative positions
- On relaunch, system displays:
- Auto-save occurs every 20 seconds
- Execution is queued
- When connection restores, code executes automatically
- Learner receives notification when results are ready
- Tap block settings icon
- Choose from color palette
- Useful for organizing complex programs
- Custom colors saved per learner
- Tap microphone icon
- Say variable name: "total score"
- System creates variable with that name
- Useful for accessibility
- Shows program flow in real-time
- Helps learners understand execution order
- Speed can be adjusted (slow/normal/fast)
- Can be paused at any block
- Animated arrows point to next action
- Speech bubbles explain each step
- "Try dragging this block here 👉"
- Tutorial can be skipped or replayed
- Star icon on blocks
- Favorites appear in "My Blocks" category
- Speeds up program building
- Tap "Convert to Code" button
- System generates Python/JavaScript
- Opens in Code Editor (if on tablet/larger screen)
- Learner can edit and learn text-based syntax
- Share session code
- Both see blocks in real-time
- Each user's cursor shown with name
- Chat feature for discussion
- Useful for pair programming
- Build program in 3 minutes
- Leaderboard for fastest correct solutions
- Bonus XP for speed
- Encourages efficiency
- Dashboard shows completed exercises
- Can view block solutions
- Progress reports
- Useful for tracking learning at home/school
- Tap "Share" button
- System generates image of blocks
- Can post to social media
- Useful for showcasing progress
- Beginner: Basic blocks only (print, variables, simple loops)
- Intermediate: Add functions, lists, conditions
- Advanced: Classes, recursion, advanced data structures
- Prevents overwhelming beginners with too many options
- Blockly editor must load within 1.5 seconds on mobile devices
- Touch targets must be at least 44x44 pixels (Apple HIG standard)
- Blocks must have high contrast for visibility in sunlight
- Pinch-to-zoom must support 50% to 200% zoom range
- Drag operations must have 150ms delay to prevent accidental moves
- Block snapping must have haptic feedback (vibration) on compatible devices
- Workspace must support up to 100 blocks without performance degradation
- App must work offline with local execution for basic exercises
- All block actions must have undo/redo support (up to 50 steps)
- Block colors must be colorblind-friendly (use patterns/icons in addition to colors)
- Text on blocks must be readable at minimum 16px font size
- Auto-save must occur every 20 seconds
- Generated code must be syntactically correct and executable
- Block toolbox must be searchable for finding specific blocks quickly
- The "Get Hint" button remains disabled until code is written.
- The learner is offered the option to view the complete solution (with loss XP reward).
- The system provides a fallback hint from the database.
- The request is logged for admin review.
- The system doesn't send to AI and displays the message.
- The system uses natural language processing to simplify the hint.
- If simplification fails, a pre-generated hint is used instead.
- First hint: Conceptual guidance only
- Second hint: Specific approach suggestion
- Third hint: Pseudocode or example structure
- Fourth hint: Partial code implementation
- Fifth hint: Complete solution with explanation
- Logic errors
- Incorrect algorithm choice
- Edge case handling
- The hint addresses these specific issues.
- The learner can view all previously received hints.
- The learner clicks "Previous Hints" to review earlier guidance.
- This helps reinforce learning without requesting duplicate hints.
- If the hint references a concept, the system includes a link to relevant lesson content.
- The learner can click to review the concept before continuing.
- AI hints must not reveal complete solutions directly.
- Hint generation must complete within 10 seconds.
- The system must track hint usage for XP calculation (fewer hints = more XP).
- Hints must be appropriate for the learner's skill level.
- The AI API must be rate-limited to prevent abuse.
- All API communications must be encrypted.
- Fallback hints must be available for all exercises.
- Implement frontend interface
- Create backend API
- Database integration
- User authentication
- Deployment instructions
- Code quality analysis (linting, formatting)
- Functionality tests (API endpoints work correctly)
- Security checks (no obvious vulnerabilities)
- Performance benchmarks (response times acceptable)
- Functionality: 40 points (all features work correctly)
- Code quality: 30 points (clean, well-documented code)
- Creativity: 15 points (innovative features, UI/UX)
- Best practices: 15 points (security, performance, structure)
- Learner's full name
- Learning path title: "Python Full-Stack Developer"
- Completion date
- Unique certificate ID (e.g., DCD-PY-2025-12345)
- Platform logo and signature
- QR code for verification
- Path details (total hours, skills acquired)
- Scanning QR code on certificate
- Entering certificate ID on verification page
- Learner name
- Path completed
- Completion date
- " This certificate is authentic and verified by DuoCodo"
- The learner can revise and resubmit (up to 3 attempts total).
- Each attempt must wait 48 hours for review.
- The system flags submission for manual review.
- Admin investigates source of similarity.
- If confirmed plagiarism:
- Submission is rejected.
- The system displays: "Your submission contains plagiarized content. Certification requires original work."
- Learner receives warning.
- Must create new project from scratch.
- Serious violations may result in temporary suspension.
- Learner must fix URLs and resubmit.
- Submission is not counted as an attempt if URLs are invalid.
- Learner can retry submission.
- Support team is notified automatically.
- Deadline is extended by 24 hours if system was at fault.
- Option 1: Retake specific path modules and retry after 30 days
- Option 2: Schedule mentorship session for guidance
- Option 3: Restart learning path from Tier 3
- The learner must choose an option to continue.
- Progress is saved but path must be re-enrolled.
- Learner can view what they completed.
- Shows remaining incomplete modules/exercises.
- "Start Final Challenge" button remains disabled.
- Provides instructions on making repository public.
- Submission is not processed until accessible.
- Bronze Certificate: 70-79 points (Pass)
- Silver Certificate: 80-89 points (Merit)
- Gold Certificate: 90-100 points (Distinction)
- Certificate design and badge reflect achievement level.
- Higher tiers may unlock additional benefits (e.g., featured portfolio, mentor access).
- Learner clicks "Add to LinkedIn" button.
- System auto-populates LinkedIn credential form:
- Credential name: "Python Full-Stack Developer"
- Issuing organization: DuoCodo
- Issue date: [Completion date]
- Credential ID: [Certificate ID]
- Credential URL: [Verification link]
- Learner confirms and posts to LinkedIn profile.
- Public portfolio page displays:
- Project demo video/screenshots
- Live project link
- GitHub repository
- Technologies used
- Project description
- Other learners can view and learn from completed projects.
- Recruiters can discover learners through project showcase.
- "Congratulate" button sends encouragement message.
- Achievement appears in community feed.
- Builds motivational community culture.
- Each completed path earns separate certificate.
- Dashboard shows all earned certificates.
- "Collection" badges for completing related paths:
- "Web Development Master" (3 web paths completed)
- "Data Science Expert" (4 data science paths completed)
- Certificates remain valid but note version: "Python Full-Stack Developer (2025)"
- Learners notified when path is significantly updated.
- Optional: Complete update modules for refreshed certificate.
- Keeps certifications current with industry standards.
- Upload list of certificate IDs.
- System validates all certificates.
- Generates report of verified credentials.
- Useful for HR departments during hiring.
- How many people completed this path
- Average completion time
- Most common career outcomes
- Salary ranges for certificate holders (if data available)
- Immutable proof of achievement.
- Cannot be forged or tampered with.
- Blockchain explorer link included.
- Future-proof credential verification.
- Professional (formal design)
- Modern (colorful, vibrant)
- Minimalist (clean, simple)
- Personalization makes certificates more meaningful.
- Certificate generation must complete within 10 seconds of passing final challenge.
- Certificates must be high-resolution (300 DPI) for printing.
- PDF certificates must be accessible (screen reader compatible).
- Certificate IDs must be cryptographically unique (collision-resistant).
- Verification URLs must remain valid indefinitely (no expiration).
- All certificate data must be backed up securely.
- The system must handle concurrent certificate generation (100+ simultaneous).
- Certificate templates must support multiple languages (English/Arabic).
- Plagiarism detection must have <5% false positive rate.
- Automated project evaluation must complete within 5 minutes.
- Manual review (if needed) must complete within 2 business days.
5.4 Sequence Diagram
Sequence diagrams were created only for casual and fully-dressed use cases, as these provide sufficient interaction detail to model system behavior. Brief use cases were excluded since they describe high-level functionality without internal system collaboration.
5.5 Class Diagram
Class diagrams are structural diagrams that show the static structure of the system, including its classes, attributes, operations, and the relationships among objects. They provide a detailed view of the system's architecture and design.
Part 1: Core User and Authentication System
This section presents the foundational classes for user management, authentication, and authorization within the DuoCodo platform. It includes user roles, profile management, and security features.
Part 2: Learning Content Management
This section illustrates the classes responsible for managing educational content, including courses, lessons, exercises, and learning paths. It shows how content is structured and organized within the platform.
Part 3: Submissions and Code Execution
This section demonstrates the classes that handle submission and code execution. It shows how the platform motivates and engages learners.
Part 4: Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
This section presents the classes that enable exercises, attempts and code analysis, including comments, discussions, friend connections, sharing capabilities, and community engagement features.
Part 5: Certification and Gamification
This section shows the classes related to certification and gamification, and validation mechanisms. It demonstrates how the platform evaluates learner competency and awards credentials.
Part 6: Administration and Platform Management
This section illustrates the classes responsible for platform administration, including system monitoring, analytics, content moderation, user management, and reporting capabilities.
Key Design Patterns and Relationships
The class diagrams above illustrate several important design patterns and relationships:
- Inheritance: User roles (Administrator, Content Creator, Learner) inherit from a base User class
- Composition: Courses are composed of Lessons, which contain Exercises
- Association: Many-to-many relationships between Learners and Courses through enrollment
- Aggregation: Learning Paths aggregate multiple Courses
- Dependency: Classes depend on authentication and authorization services
These diagrams provide a comprehensive view of the DuoCodo platform's architecture, showing how different components interact to deliver a complete learning experience.
Chapter 6: Database Design
6.1 Entity Relationship Diagram
Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD) represent the data model of the DuoCodo platform, showing the entities, their attributes, and the relationships between them. This comprehensive database design ensures data integrity, efficient querying, and scalability.
Part 1: User Management and Authentication
This section presents the core entities for user management, including user accounts, roles, authentication mechanisms, and profile information. It establishes the foundation for user identity and access control.
Part 2: Learning Content and Course Structure
This section illustrates the entities related to educational content organization, including courses, lessons, modules, exercises, and learning paths. It shows how content is structured and interconnected within the platform.
Part 3: Submissions and Code Execution
This section demonstrates the entities that track submission and code execution. It shows how the platform motivates learners through gamification elements.
Part 4: Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
This section shows the entities for exercises, attempts and code analysis. It demonstrates how the platform evaluates learner competency and issues credentials.
Part 5: Certification and Gamification
This section presents the entities that enable certification and gamification, including comments, discussions, friend connections, notifications, sharing, and community engagement features.
Part 6: Administration and System Management
This section illustrates the entities for platform administration, including system logs, analytics, content moderation, reports, backups, and monitoring capabilities.
Database Design Principles
The ERD design follows these key principles:
- Normalization: Entities are normalized to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity
- Referential Integrity: Foreign key relationships ensure data consistency across tables
- Scalability: Design supports horizontal and vertical scaling for growing user base
- Performance: Indexed fields and optimized relationships for efficient queries
- Flexibility: Schema allows for future extensions and feature additions
- Security: Sensitive data fields include encryption and access control mechanisms
These diagrams provide a comprehensive view of the DuoCodo platform's data architecture, showing how information is stored, organized, and related to support all system functionalities.
6.2 Database Schema
Database Schema represents the logical structure of the DuoCodo platform database, showing tables, columns, data types, constraints, and relationships. This detailed schema design ensures optimal performance, data integrity, and supports all platform functionalities.
Part 1: User Management and Authentication
This section presents the database tables for user management, including user accounts, roles, authentication mechanisms, and profile information. It establishes the foundation for user identity and access control with detailed field specifications.
Part 2: Learning Content and Course Structure
This section illustrates the database tables related to educational content organization, including courses, lessons, modules, exercises, and learning paths. It shows how content is structured and stored within the database with proper data types and constraints.
Part 3: Submissions and Code Execution
This section demonstrates the database tables that track learner progress, achievements, experience points (XP), badges, streaks, and leaderboard rankings. It shows how the platform stores and manages gamification elements with appropriate indexing.
Part 4: Exercises, Attempts and Code Analysis
This section shows the database tables for quizzes, assessments, test cases, submissions, grading, and certifications. It demonstrates how the platform stores evaluation data and manages credentials with proper validation constraints.
Part 5: Certification and Gamification
This section presents the database tables that enable social interactions, including comments, discussions, friend connections, notifications, sharing, and community engagement features with optimized query structures.
Part 6: Administration and System Management
This section illustrates the database tables for platform administration, including system logs, analytics, content moderation, reports, backups, and monitoring capabilities with appropriate data retention policies.
Database Schema Specifications
The database schema implementation follows these key specifications:
- Data Types: Appropriate data types chosen for optimal storage and performance
- Constraints: Primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and check constraints ensure data integrity
- Indexing: Strategic indexes on frequently queried columns for optimal performance
- Normalization: Tables normalized to 3NF (Third Normal Form) to eliminate redundancy
- Referential Integrity: Foreign key relationships maintain consistency across related tables
- Security: Sensitive fields include encryption specifications and access control measures
- Scalability: Schema design supports partitioning and sharding for future growth
- Backup Strategy: Tables include timestamp fields for incremental backup operations
This detailed schema provides the implementation blueprint for the DuoCodo platform's database, ensuring robust data management and optimal query performance across all system components.
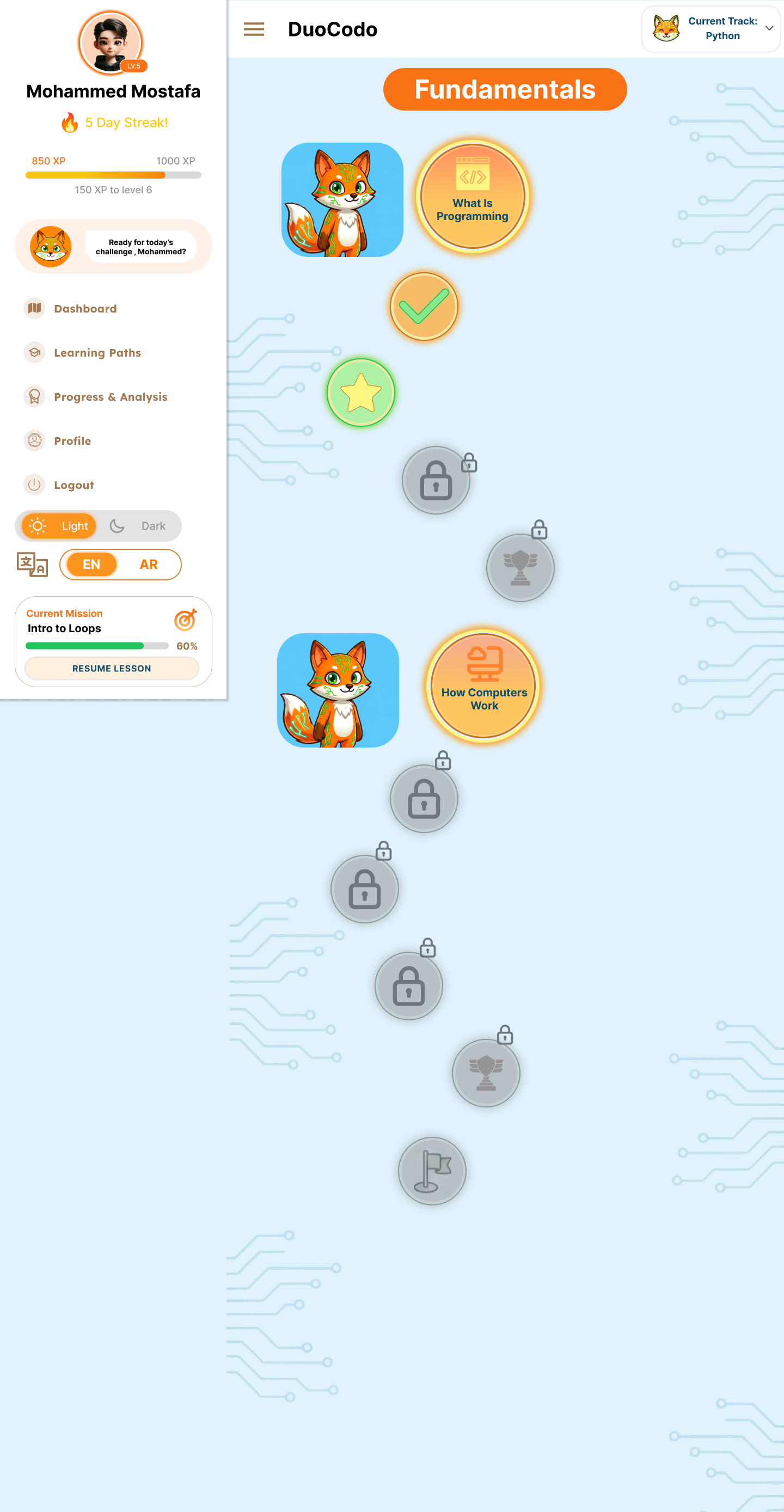
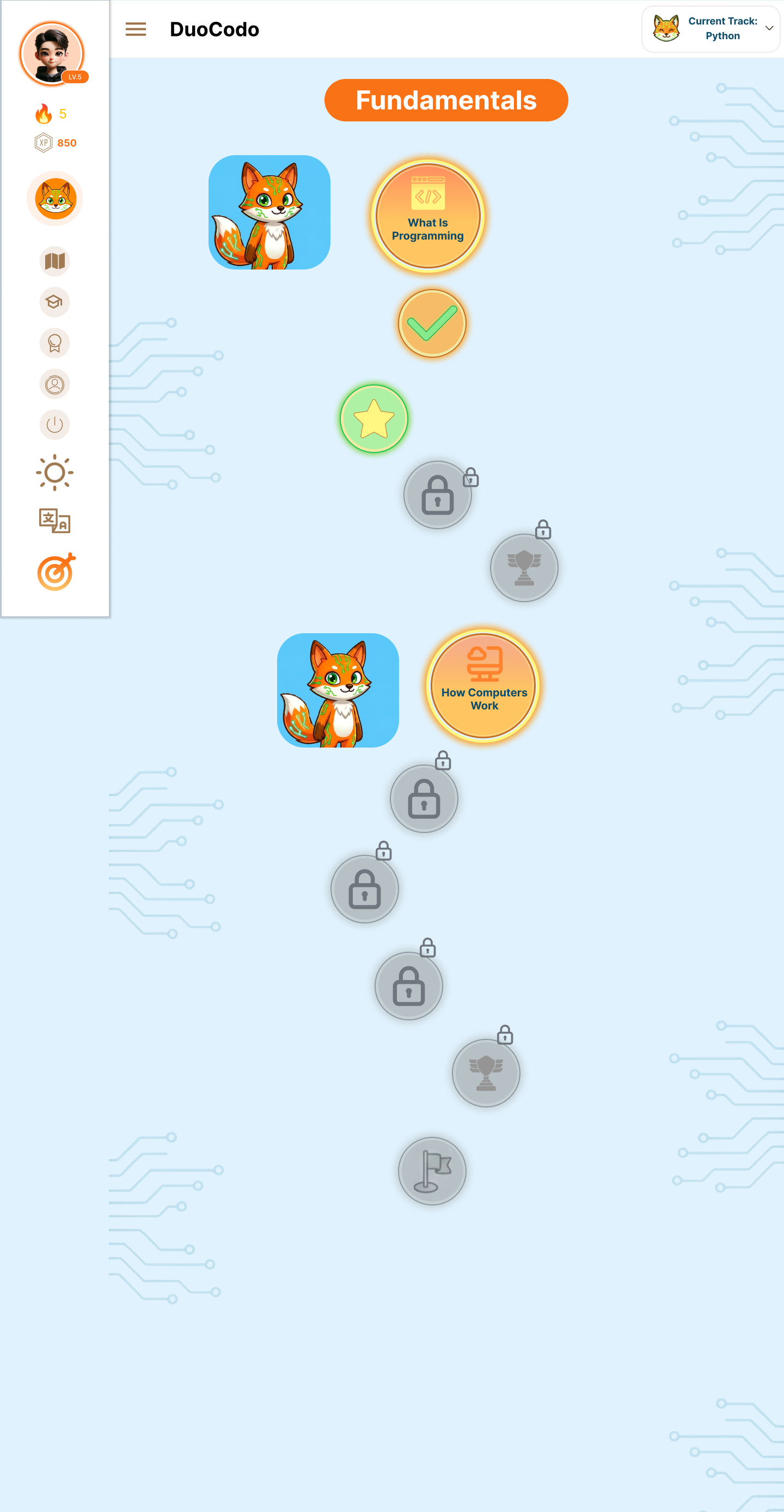
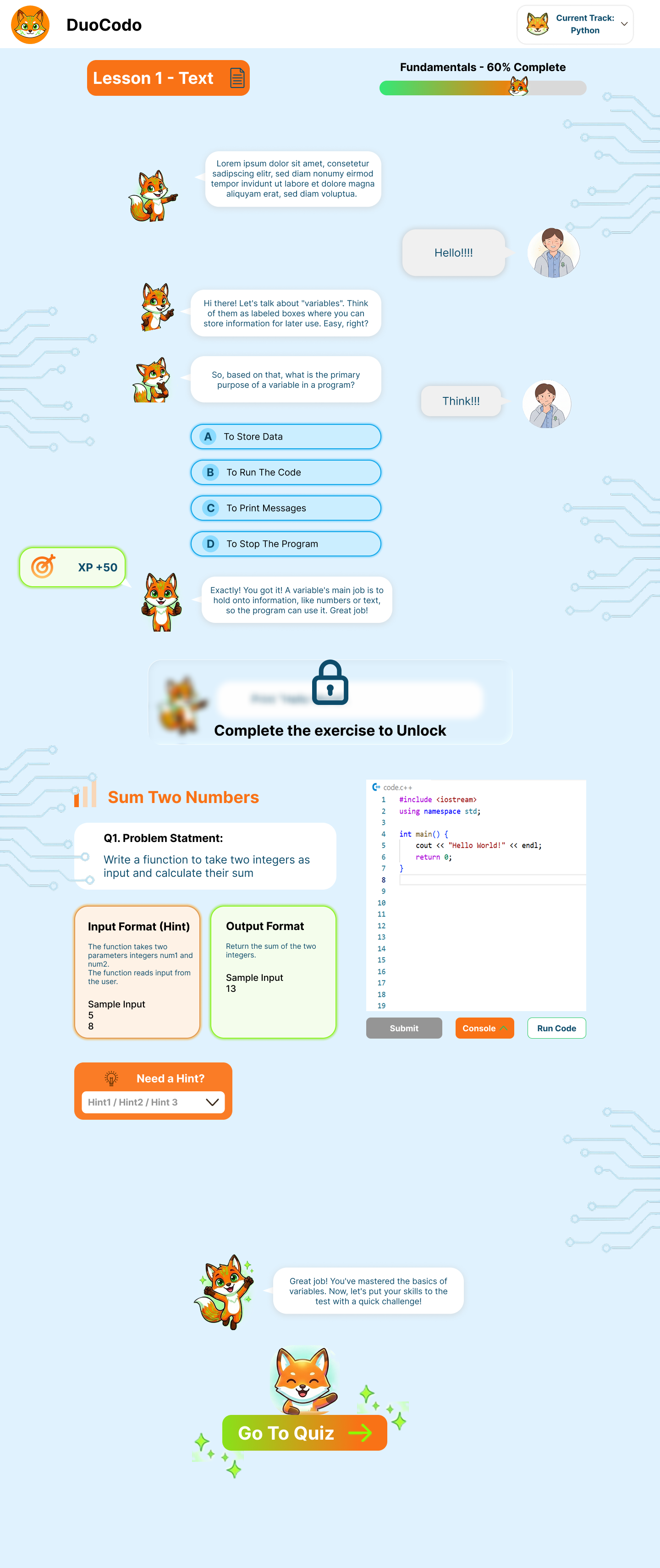
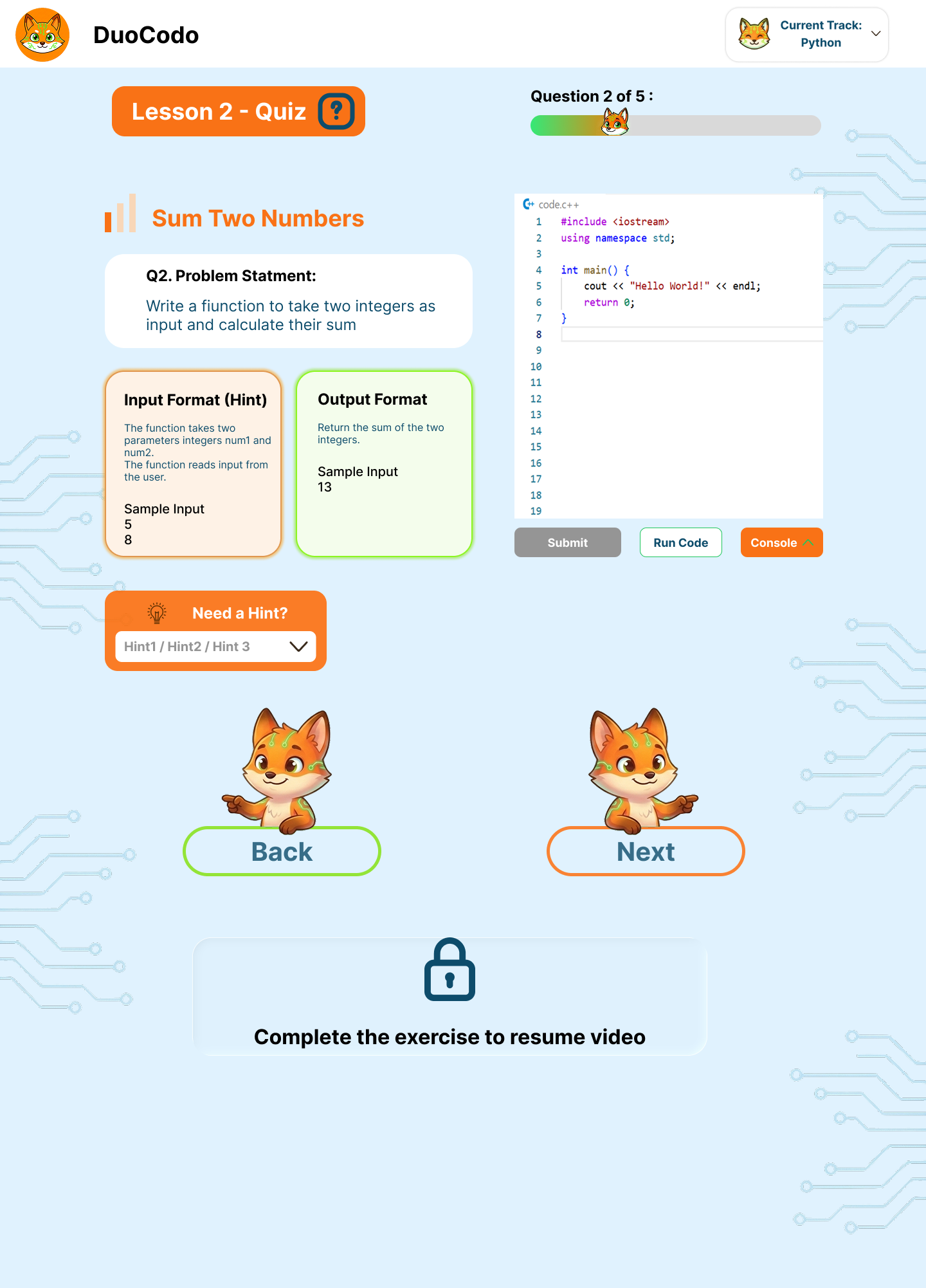
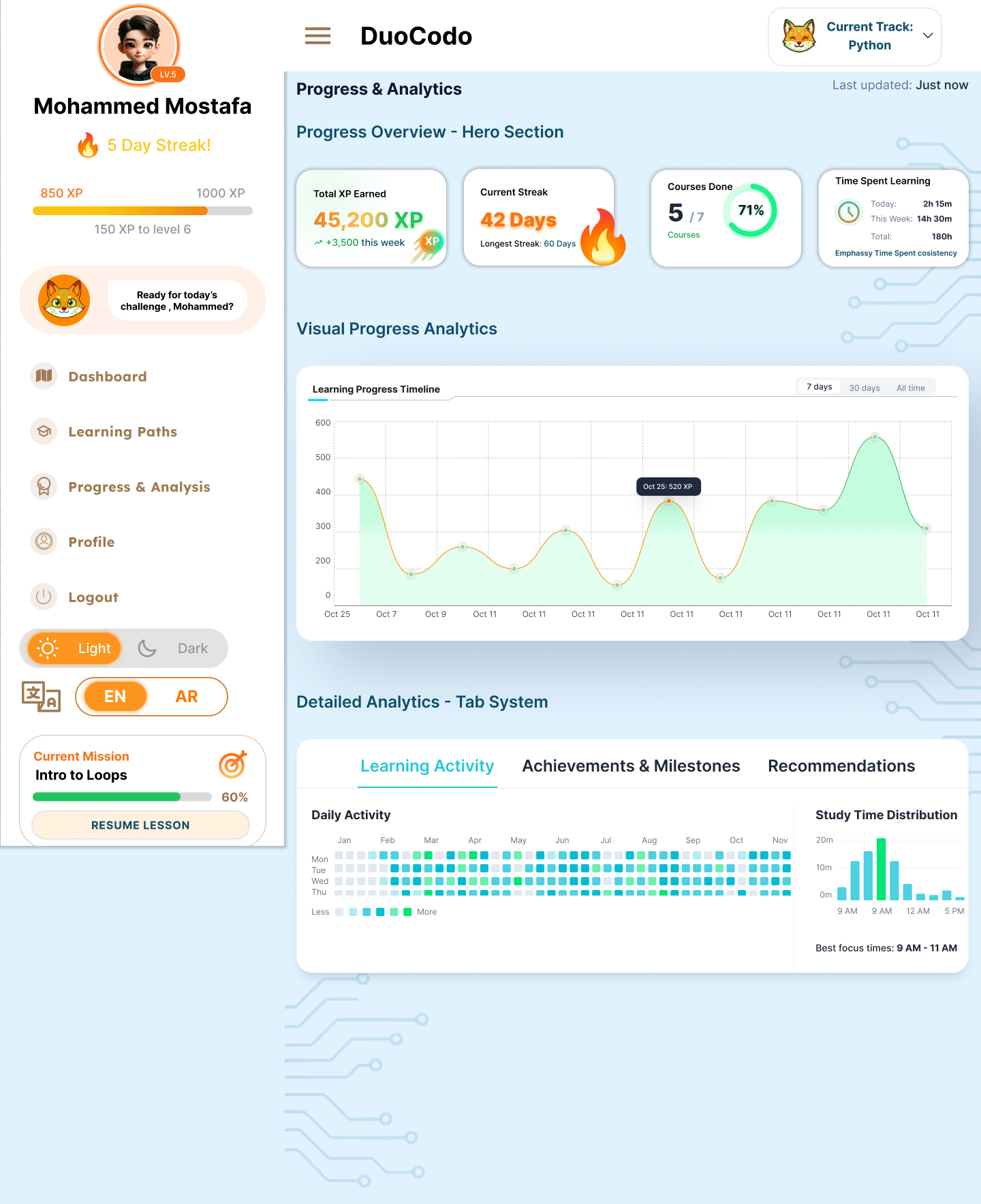
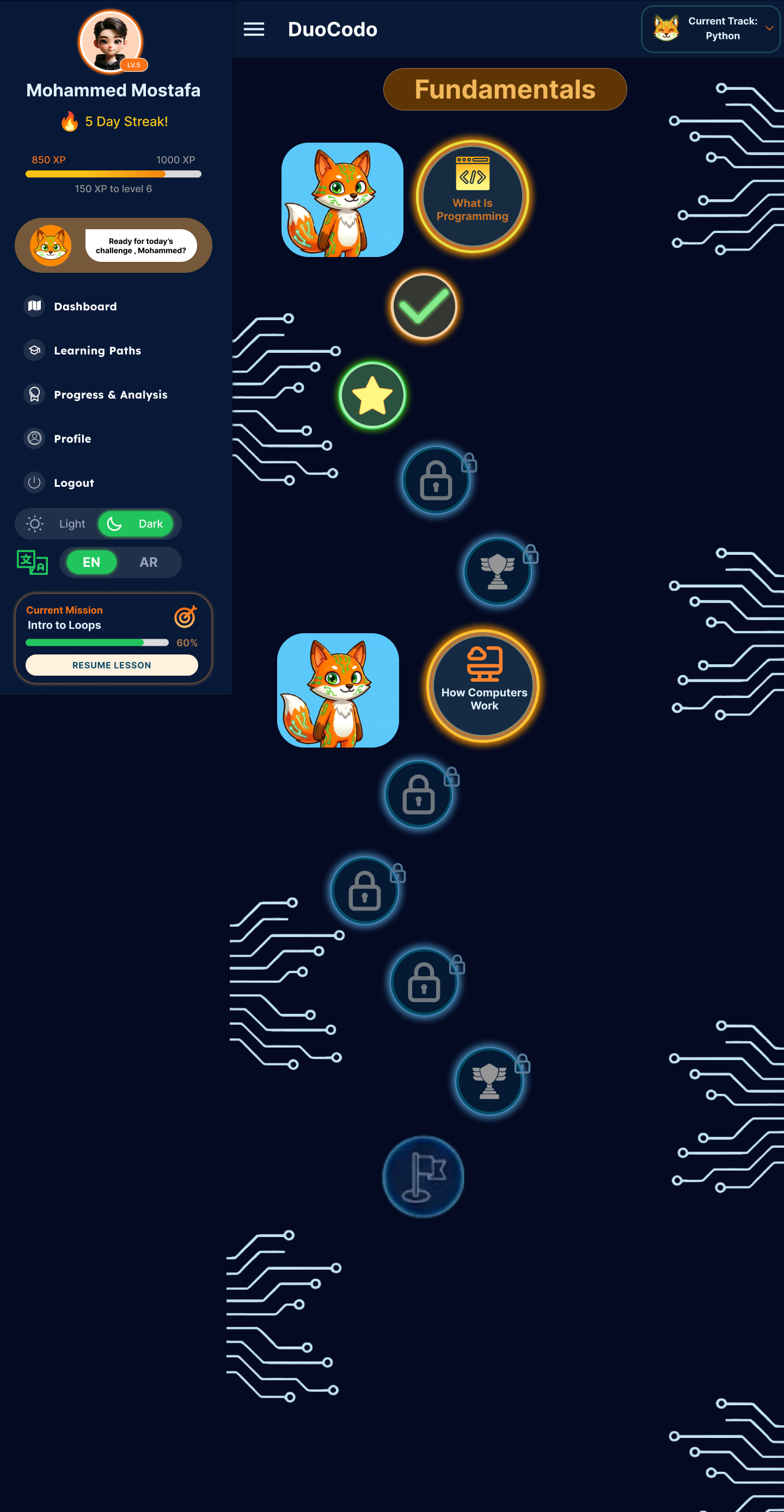
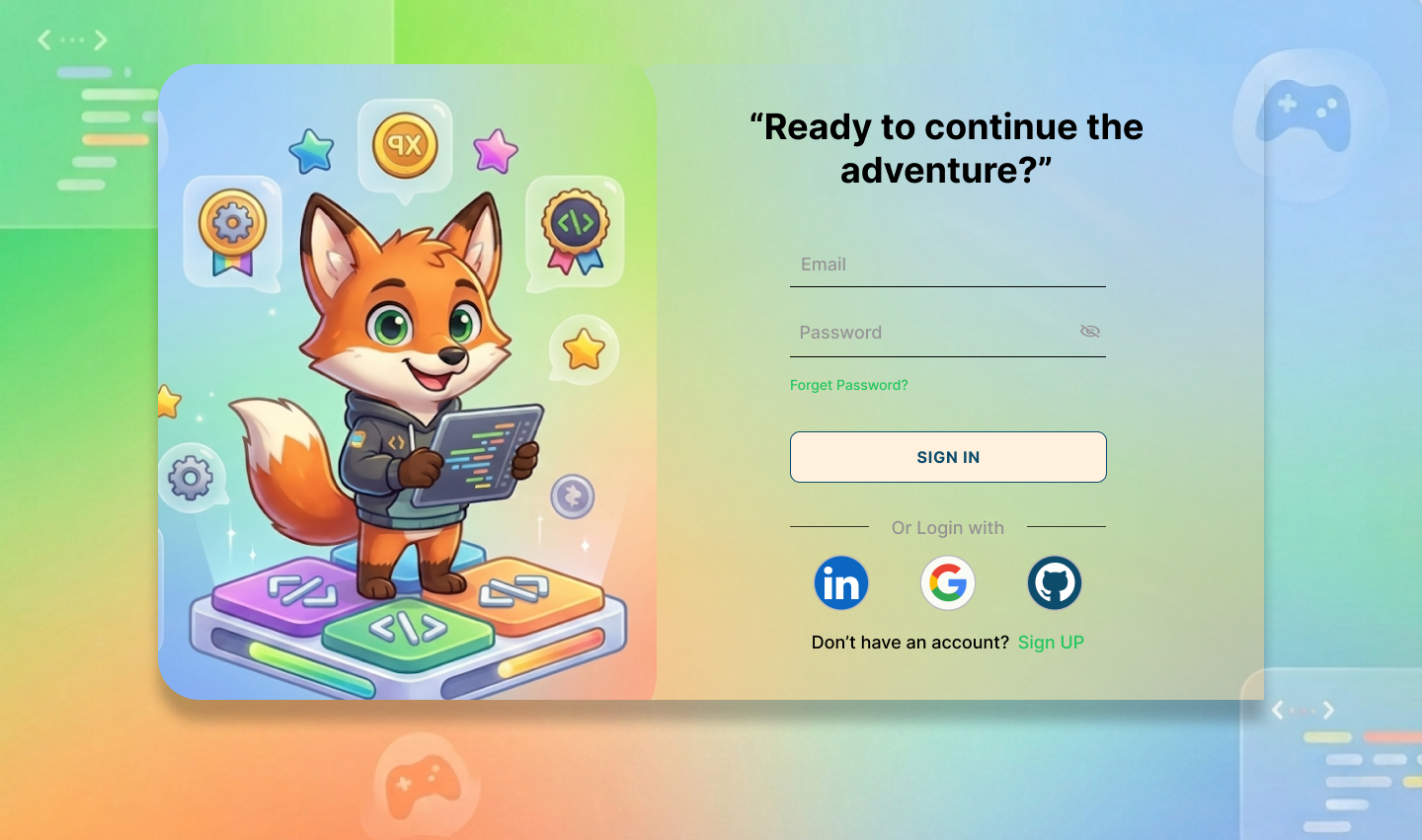
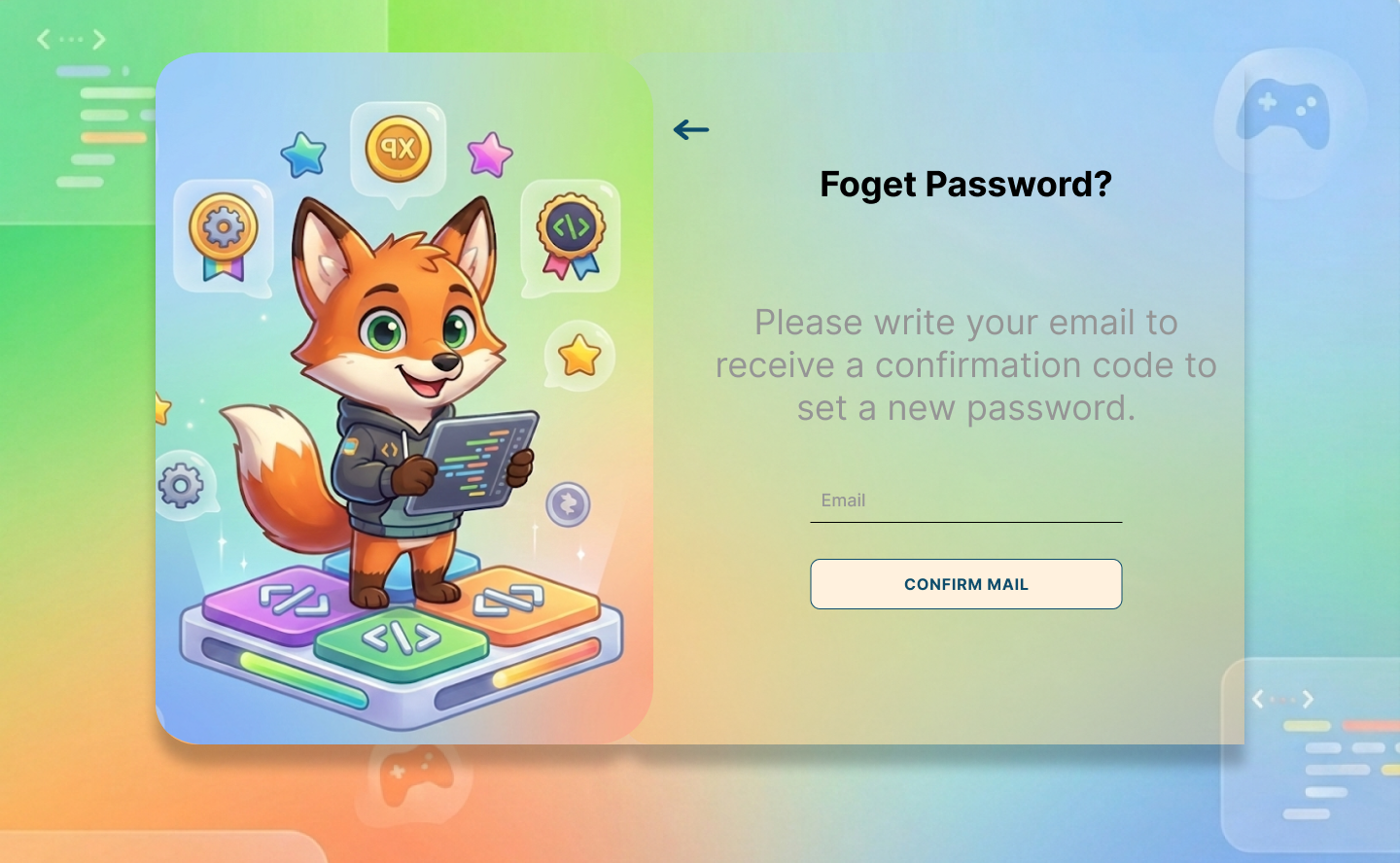
Chapter 7: User Interface
7.1 Authentication Screens



7.2 Main Dashboard